The gene editing technique CRISPR/Cas9 has allowed researchers to make precise and impactful changes to an organism’s DNA to fix mutations that cause genetic disease.
Read the full article at: www.news-medical.net

The gene editing technique CRISPR/Cas9 has allowed researchers to make precise and impactful changes to an organism’s DNA to fix mutations that cause genetic disease.
Read the full article at: www.news-medical.net

Researchers discovered a potential link between “endogenous retroviruses” present in the human genome and the development of neurodegenerative diseases.
Summary: Researchers discovered a potential link between “endogenous retroviruses” present in the human genome and the development of neurodegenerative diseases. Their study found that these ancient viral remnants might influence the spread of protein aggregates commonly associated with certain dementias. While these retroviruses don’t trigger neurodegeneration, they may exacerbate the disease process. This discovery offers new potential therapeutic avenues, such as suppressing gene expression or neutralizing viral proteins.
Research cited published in Nature (Aug. 18, 2023):
Read the full article at: neurosciencenews.com

An autonomous drone has competed against human drone-racing champions — and won. The victory can be attributed to savvy engineering and a type of artificial intelligence that learns mostly through trial and error.
First-person view (FPV) drone racing is a televised sport in which professional competitors pilot high-speed aircraft through a 3D circuit. Each pilot sees the environment from the perspective of their drone by means of video streamed from an onboard camera. Reaching the level of professional pilots with an autonomous drone is challenging because the robot needs to fly at its physical limits while estimating its speed and location in the circuit exclusively from onboard sensors.
Here the authors of this paper introduce Swift, an autonomous system that can race physical vehicles at the level of the human world champions. The system combines deep reinforcement learning (RL) in simulation with data collected in the physical world. Swift competed against three human champions, including the world champions of two international leagues, in real-world head-to-head races. Swift won several races against each of the human champions and demonstrated the fastest recorded race time.
This work represents a milestone for mobile robotics and machine intelligence, which may inspire the deployment of hybrid learning-based solutions in other physical systems. An autonomous system is described that combines deep reinforcement learning with onboard sensors collecting data from the physical world, enabling it to fly faster than human world champion drone pilots around a race track.
Read the full article at: www.nature.com
A team of experts at University College London are working to make drugs more palatable – and at a speed never seen before
Read the full article at: www.telegraph.co.uk
Rochester Institute of Technology researchers are improving non-invasive treatment options for degenerative disc disease, an ailment that impacts 3 million adults yearly in the U.S., according to the Mayo Clinic.
Read the full article at: www.news-medical.net

Illinois passed a law to protect child influencers. Advocates are cautiously optimistic more states will follow.
Read the full article at: www.nbcnews.com

An independent report found NASA could be key in collecting data about UFOs and aid in the effort to explain the phenomena.
Read the full article at: www.cnn.com
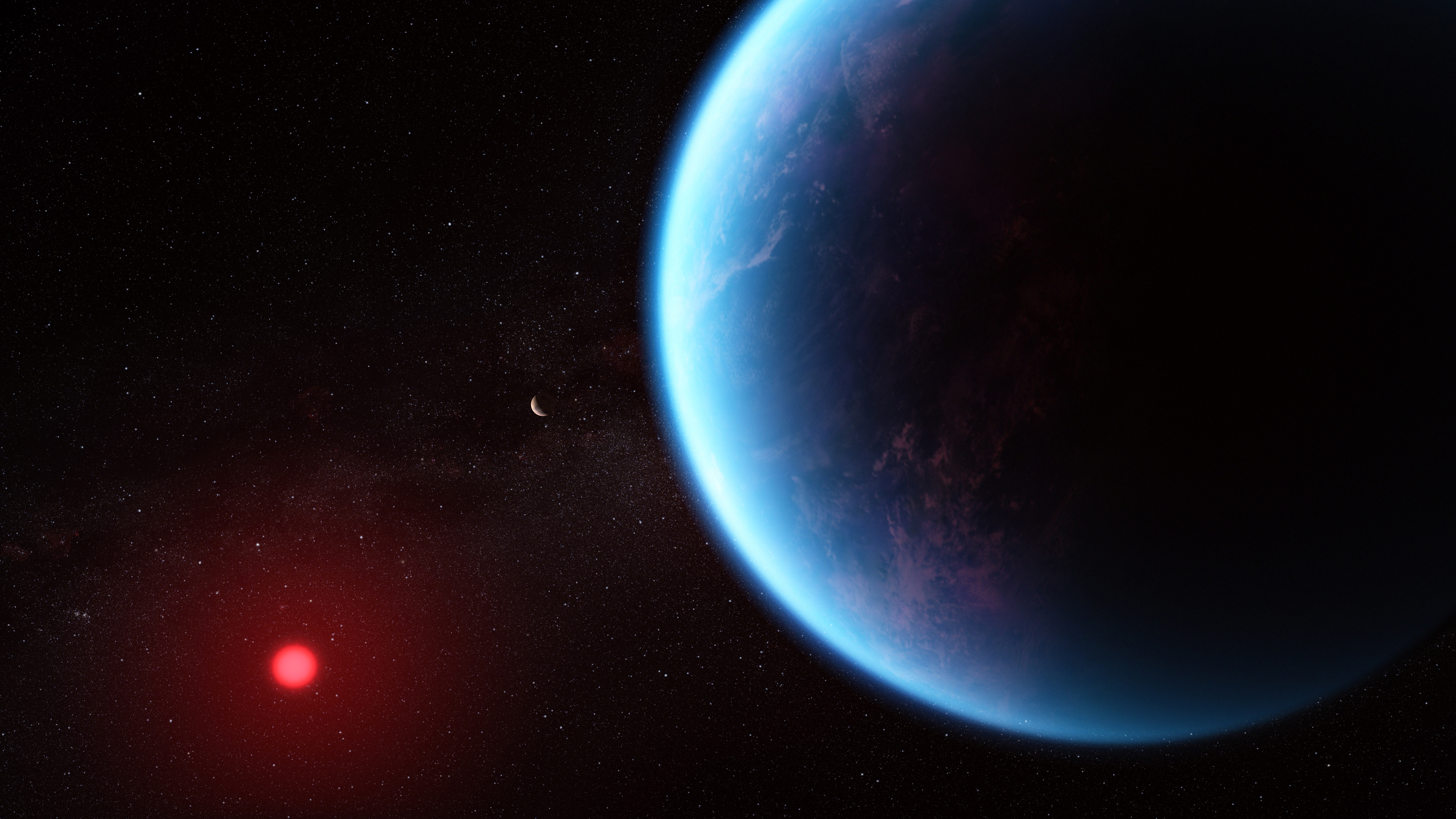

A new investigation with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope into K2-18 b, an exoplanet 8.6 times as massive as Earth, has revealed the presence of carbon-bearing molecules including methane and carbon dioxide.
Read the full article at: www.nasa.gov

Your initial encounter with AI might have introduced you to ChatGPT, the OpenAI AI-chatbot with an astonishing ability to answer a wide array of questions. From crafting poems and resumes to concocting fusion recipes, the prowess of ChatGPT has been likened to a turbocharged autocomplete feature.
Yet, AI chatbots are just a fraction of the broader AI landscape. While it’s impressive to have ChatGPT assist with homework or watch Midjourney generate captivating mech images inspired by their country of origin, the potential of AI extends far beyond. This potential, valued at approximately $4.4 trillion annually for the global economy by the McKinsey Global Institute, underscores the growing significance of artificial intelligence.
As society becomes increasingly intertwined with AI, novel terms are cropping up everywhere. Whether you’re aiming to engage in intelligent conversations or excel in a job interview, acquainting yourself with these essential AI terms is crucial.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): A concept alluding to a more advanced AI version than what currently exists, capable of outperforming humans in tasks while also enhancing its own capabilities.
AI Ethics: Principles designed to prevent AI from causing harm to humans, often achieved through determining how AI systems should handle data collection and address bias.
AI Safety: An interdisciplinary field focused on the long-term consequences of AI and the potential rapid emergence of super-intelligent AI that could pose risks to humanity.
Algorithm: A set of instructions enabling a computer program to learn from and analyze data, aiding in recognizing patterns and autonomously completing tasks.
Alignment: Adjusting AI to achieve desired outcomes, spanning from moderating content to promoting positive human interactions.
Anthropomorphism: The tendency to attribute human-like attributes to non-human entities. In the context of AI, this refers to perceiving chatbots as more human-like and aware than they truly are.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): The utilization of technology to simulate human intelligence, either within computer programs or robotics. A computer science field dedicated to developing systems capable of human-like tasks.
Bias: In relation to large language models, inaccuracies stemming from training data that lead to false associations between certain characteristics and specific groups.
Chatbot: A program that interacts with humans through text, mimicking human language.
ChatGPT: An AI chatbot developed by OpenAI employing extensive language model technology.
Cognitive Computing: A synonym for artificial intelligence.
Data Augmentation: The process of remixing existing data or introducing a diverse dataset to train AI models.
Deep Learning: A subset of machine learning involving intricate patterns recognition in visuals, audio, and text using multiple parameters. Inspired by the human brain, it employs artificial neural networks to detect patterns.
Diffusion: A machine learning technique introducing random noise to existing data, often used to train models to recreate or recover input data.
Emergent Behavior: Instances where an AI model demonstrates unexpected abilities.
End-to-End Learning (E2E): A deep learning approach where a model learns to perform a task in its entirety, solving the problem holistically.
Ethical Considerations: An awareness of the ethical implications and concerns related to AI, encompassing privacy, data usage, fairness, misuse, and safety issues.
Foom (Fast Takeoff): The notion that AGI development might advance too swiftly to a point where humanity’s safety could be compromised.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): AI models composed of two neural networks – a generator and a discriminator – creating and validating new data, respectively.
Generative AI: Technology utilizing AI to craft content like text, videos, code, or images by discerning patterns and generating original responses.
Google Bard: A Google AI chatbot similar to ChatGPT, but it extracts information from current web sources while ChatGPT is limited to data until 2021 and lacks internet connectivity.
Guardrails: Policies and constraints imposed on AI models to ensure responsible data handling and prevent the generation of disturbing content.
Hallucination: Incorrect AI responses, including generative AI producing confident but erroneous answers.
Large Language Model (LLM): An AI model trained on extensive text data to comprehend language and generate human-like content.
Machine Learning (ML): An AI component allowing computers to learn and predict outcomes without explicit programming, often paired with training sets to generate fresh content.
Microsoft Bing: Microsoft’s search engine employing AI-powered search results similar to Google Bard, connected to the internet.
Multimodal AI: AI capable of processing diverse inputs such as text, images, videos, and speech.
Natural Language Processing: A branch of AI utilizing machine learning and deep learning to enable computers to comprehend human language, often employing learning algorithms, statistical models, and linguistic rules.
Neural Network: A computational model mirroring the human brain’s structure, designed to identify data patterns. Comprising interconnected nodes or neurons, it evolves with time.
Overfitting: A machine learning error when a model closely mirrors training data but struggles with new data.
Parameters: Numerical values shaping the behavior and structure of LLMs, facilitating predictions.
Prompt Chaining: AI’s ability to leverage previous interactions for context in future responses.
Stochastic Parrot: An analogy illustrating that LLMs lack a comprehensive understanding of language’s meaning and context, akin to a parrot mimicking words without grasping their significance.
Style Transfer: The process of adapting one image’s style to another’s content, enabling AI to apply visual attributes from one image to another.
Temperature: Parameters influencing the randomness of language model output. Higher values yield more daring responses.
Text-to-Image Generation: Producing images based on textual descriptions.
Training Data: Datasets utilized to educate AI models, encompassing text, images, code, and data.
Transformer Model: A deep learning model learning context by deciphering relationships within data, like sentences or image components. Unlike sequential analysis, it comprehends context holistically.
Turing Test: Evaluates a machine’s human-like behavior, passing if humans can’t distinguish its responses from humans’.
Weak AI (Narrow AI): AI focused on specific tasks, unable to surpass its designated skill set. Most contemporary AI falls into this category.
Zero-Shot Learning: A test requiring a model to complete tasks without specific training data, e.g., recognizing a lion based on knowledge of tigers.
Read the full article at: www.weeklyblitz.net

By allowing the use of AI tools proven to be safe, but requiring them to be used within explicit guidelines, you can alleviate both employee frustration and organizational risk.
Read the full article at: www.infoworld.com