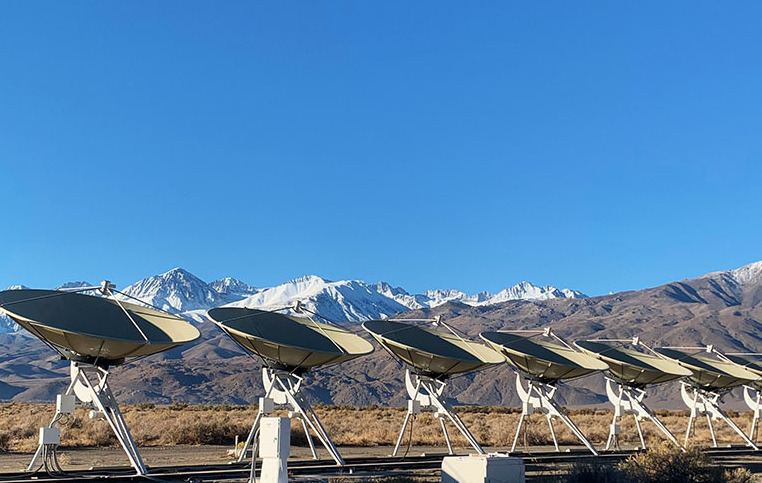
When the immense Arecibo radio telescope in Puerto Rico collapsed in 2020, it left gaping holes in astronomy. Now, a team from the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) hopes to address some of the gaps with a very different instrument: a tightly packed array of relatively inexpensive radio dishes that aims to quickly image radio sources across wide swaths of the sky. A nearly completed prototype array in California that the team calls a “radio camera” is already locating dozens of the distant, enigmatic eruptions called fast radio bursts (FRBs). Next year, the team hopes to begin construction on a much larger array with 2000 dishes that, together, will match the size of Arecibo.
Maura McLaughlin of West Virginia University is a leader of NANOGrav (the North American Nanohertz Observatory for Gravitational Waves), an effort to search for gravitational waves from supermassive black holes that relied on Arecibo for half its data. She says they took “a big sensitivity hit” when it was lost. “We really need a new telescope with a similar collecting area,” she says, and Caltech’s planned Deep Synoptic Array (DSA) fits that bill. “It will be a game changer.”
To gain sensitivity, radio astronomers can build big dishes like Arecibo or arrays of smaller dishes. But in most such arrays, the dishes are widely spaced, which sharpens their resolution but creates “a data deluge problem,” says Caltech’s Gregg Hallinan, DSA principal investigator (PI). Producing an image from a scattered array is like looking through a fragmented mirror, he says, and recreating the information from the missing parts is a complex nonlinear process known as deconvolution that can take weeks—or even years.
Many astronomers just want to regularly survey the sky for new objects or monitor sources for subtle changes without a heavy processing burden. Caltech’s solution, Hallinan says, is to “fill the mirror up” by packing low-cost dishes together. That makes deconvolution easier and should enable DSA to construct images in real time. The team has nearly finished assembling its prototype, the DSA-110, a T-shaped array of 95 dishes spaced 1 meter apart at Caltech’s Owens Valley Radio Observatory in California plus another 15 “outriggers” spread out more than a kilometer distant. To keep construction costs to $4 million, the instrument uses commercially available 4.6-meter dishes, homemade amplifiers, and wave-channeling feeds fashioned out of cake tins. Most radio telescopes require expensive cryogenic cooling to reduce amplifier noise, but Caltech’s engineers have squeezed similar performance out of room-temperature circuits. Co-PI Vikram Ravi admits they perform less well in the summer heat.
With a wide field of view, DSA-110 is good at detecting FRBs, intense blasts of radio waves lasting only milliseconds, coming from all over the sky. Several thousand have been detected, but little more than a dozen have been traced to their home galaxies, which might hold clues to what is powering the bursts. DSA-110 aims to localize many more. If a burst is detected, data from the outrigger dishes allow the telescope to zoom in and pin the FRB to its galaxy.
Read the full article at: www.science.org


 As the name suggests, Martin Mirakyan is exploring the Python programming language for over 100 days. He starts from a complete beginner level to make sure people without any programming background can get started and follow along. Then he gradually covers more advanced concepts such as task automation, data visualization, and web scraping and performs some basic data-science experiments.
As the name suggests, Martin Mirakyan is exploring the Python programming language for over 100 days. He starts from a complete beginner level to make sure people without any programming background can get started and follow along. Then he gradually covers more advanced concepts such as task automation, data visualization, and web scraping and performs some basic data-science experiments.